Find the Right Care, Right Away
Care on Demand
Skip the drive, go online, and get the care you need from the comfort of home.
Start Your VisitOnline Scheduling
Book your next visit from your smartphone or computer. It’s that easy.
Schedule NowPrimary Care
Saint Alphonsus provides a full range of medical services in Idaho and Oregon.
Schedule NowFind a Doctor
The right care begins with the right physician. Find the right provider here.
Schedule NowPay My Bill
Saint Alphonsus offers you an easy and secure method of paying your bills, including online and by mail.
MyChart Portal
The MyChart patient portal makes it easy to stay connected to your health.
Access Medical Records
We offer a variety of ways to access your health records including online and by phone.
What would you like to do?
Flexibility & Convenience
You want health care that's easy and convenient. We do too. At Saint Alphonsus, we offer a variety of ways to access care the care you need.


Request an Appointment
Put your health first and request an appointment with a primary care or specialty care provider.
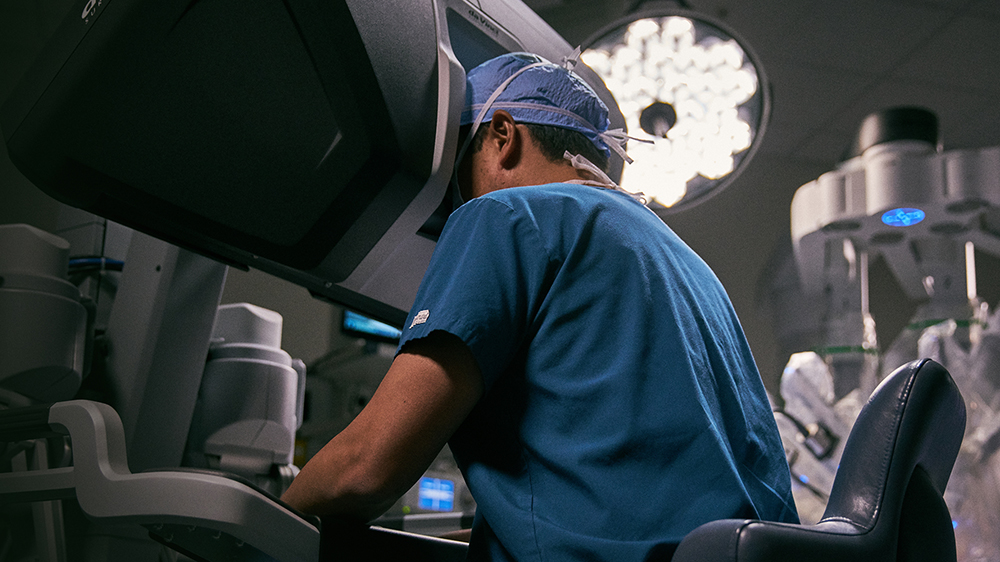
More Precision, Less Incision
Bringing the latest in robotic-assisted surgery to the Treasure Valley and Eastern Oregon. For our surgeons, that means more clarity, dexterity, and precision. For our patients, that means less pain, less blood loss, less complications, less scarring, and less time recovering.

Schedule Online, Anytime
Book your next visit from your smartphone or computer – it’s that easy.
Join Our Team
Quickly apply below and our recruitment team will reach out to see if we have a job fit for you now or in the future!












